
5G and Its Implications for Future Wireless Communication Standards
The advent of 5G technology represents a transformative leap in the realm of wireless communication. As the fifth generation of mobile networks, 5G promises unprecedented speeds, lower latency, and enhanced connectivity, fundamentally altering the way we interact with technology. This article delves into the intricacies of 5G, its current impact, and its far-reaching implications for future wireless communication standards.
1. Introduction to 5G Technology
5G, or fifth-generation wireless technology, is the latest iteration of mobile network technology, following 4G (LTE). It is designed to meet the growing demands for higher data rates, increased connectivity, and lower latency, addressing limitations that previous generations could not overcome. Unlike its predecessors, 5G is not just an incremental improvement but a revolutionary advancement that introduces a new architecture and new capabilities.
Key Features of 5G:
- Enhanced Data Speeds: 5G networks offer data speeds that are up to 100 times faster than 4G LTE. Theoretical maximum speeds can exceed 10 Gbps, though real-world speeds are somewhat lower.
- Reduced Latency: Latency, or the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination, is significantly reduced in 5G networks, reaching as low as 1 millisecond compared to 30-50 milliseconds in 4G.
- Increased Capacity: 5G supports a higher density of connections per square kilometer, enabling more devices to be connected simultaneously without degradation of network performance.
- Improved Reliability: Enhanced reliability and stability in connections are crucial for mission-critical applications and services.
2. Technological Foundations of 5G
5G technology is built on several key innovations and principles:
- Millimeter Waves (mmWave): 5G utilizes higher frequency bands, known as millimeter waves, which offer greater bandwidth and capacity. These frequencies range from 24 GHz to 100 GHz. However, mmWave signals have limited range and can be obstructed by buildings and other obstacles, necessitating the deployment of more small cells.
- Small Cells: To address the range limitations of mmWave frequencies, 5G networks deploy a dense array of small cells—compact base stations placed closer together than traditional cell towers. These small cells are essential for ensuring consistent coverage and high speeds.
- Network Slicing: 5G introduces the concept of network slicing, which allows for the creation of virtualized, isolated network segments tailored to specific applications or services. Each slice can be optimized for different requirements, such as ultra-low latency for autonomous vehicles or high bandwidth for video streaming.
- Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output): Massive MIMO technology involves equipping base stations with a large number of antennas to improve signal quality, capacity, and efficiency. This technology enhances the ability of the network to handle multiple users simultaneously.
- Beamforming: Beamforming is a technique used to direct radio signals more precisely towards users rather than broadcasting in all directions. This improves signal strength, reduces interference, and increases overall network efficiency.
3. Current Impact of 5G
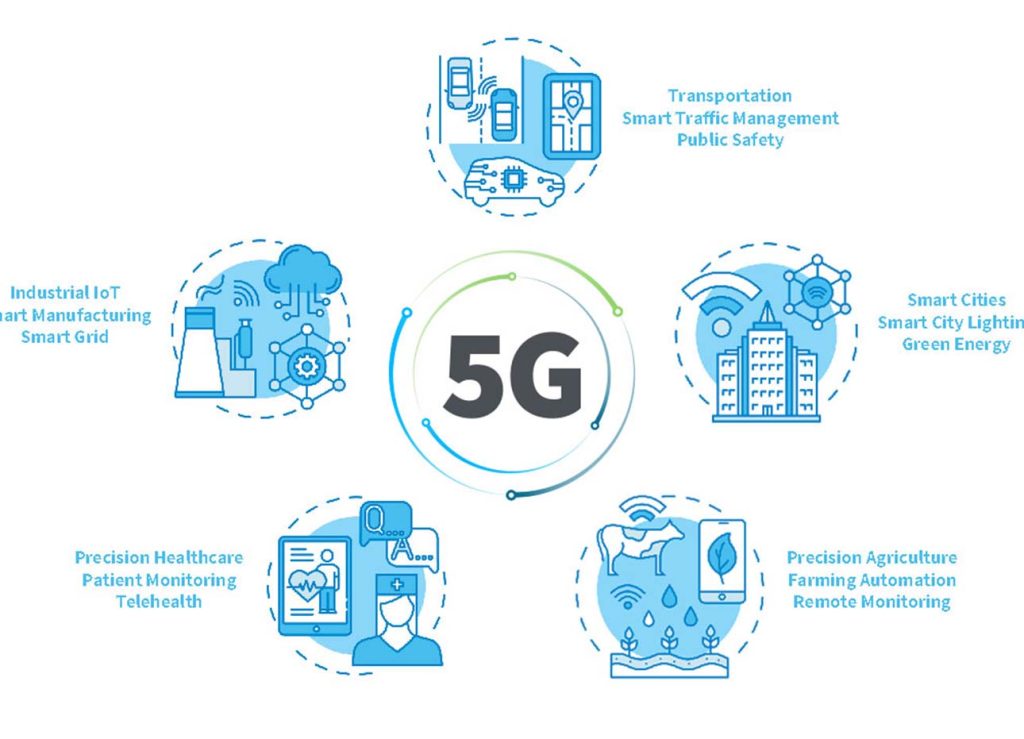
The deployment of 5G networks is already having a significant impact on various sectors:
- Consumer Electronics: 5G enhances the performance of smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices, providing faster download and upload speeds, better video quality, and more reliable connections.
- Healthcare: 5G enables advancements in telemedicine, remote surgery, and real-time patient monitoring. High-speed connectivity allows for the transmission of large medical imaging files and supports the operation of remote medical devices.
- Transportation: In the automotive industry, 5G facilitates the development of autonomous vehicles by providing low-latency communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and traffic management systems. This connectivity enhances safety and efficiency on the roads.
- Smart Cities: 5G plays a critical role in the development of smart cities by supporting a wide range of applications, including smart grids, intelligent transportation systems, and environmental monitoring. It enables the seamless integration of various IoT devices and systems.
- Entertainment and Media: The high speeds and low latency of 5G improve streaming quality for video content, enable immersive experiences in virtual and augmented reality, and support interactive gaming with minimal lag.
4. Implications for Future Wireless Communication Standards
The advent of 5G is poised to influence the evolution of future wireless communication standards in several ways:
- 6G Development: As 5G establishes the groundwork for future advancements, research into the next generation—6G—has already begun. 6G is expected to push the boundaries further, aiming for even higher speeds, lower latency, and more advanced capabilities such as holographic communication and seamless integration of AI.

- Increased Focus on Spectrum Efficiency: The demand for spectrum is growing, and future wireless standards will need to focus on more efficient use of available frequencies. This involves advanced techniques for spectrum sharing, dynamic spectrum access, and utilization of higher frequency bands.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Future wireless standards will likely integrate more closely with emerging technologies such as quantum computing, AI, and blockchain. These integrations could enhance network security, optimize performance, and enable new applications.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: As wireless networks become more critical to various sectors, ensuring robust security will be paramount. Future standards will need to incorporate advanced encryption methods, threat detection mechanisms, and privacy protections to safeguard sensitive data.
- Global Harmonization: Achieving global harmonization of wireless standards is essential for interoperability and seamless connectivity. Efforts will continue to align technical standards across different regions and ensure that devices and networks can operate effectively worldwide.
5. Challenges and Considerations
While 5G offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges and considerations:
- Infrastructure Requirements: The deployment of 5G requires significant investment in new infrastructure, including the installation of small cells, upgrading backhaul systems, and developing new technologies. This investment is essential to realize the full potential of 5G.
- Regulatory and Policy Issues: The implementation of 5G involves navigating complex regulatory and policy landscapes, including spectrum allocation, health and safety concerns, and coordination with various stakeholders. Policymakers and industry leaders must work together to address these issues.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: The increased connectivity of devices and systems raises concerns about data privacy and security. Ensuring that 5G networks are secure from cyber threats and protecting user data will be critical to maintaining trust in the technology.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of deploying and operating 5G infrastructure, including the energy consumption of networks and electronic waste, must be carefully managed. Sustainable practices and energy-efficient technologies will be essential.
5G represents a monumental leap forward in wireless communication technology, offering transformative benefits across various sectors. Its implications for future wireless communication standards are profound, setting the stage for even more advanced generations of technology. As 5G continues to roll out globally, it will shape the development of future wireless standards, drive innovation, and redefine the way we connect and interact with the world.
The journey towards 6G and beyond is already underway, with researchers and engineers working to address the challenges and seize the opportunities presented by 5G. By understanding and leveraging the capabilities of 5G, we can unlock new possibilities and create a more connected, efficient, and intelligent future.

