Dual-Screen Smartphones: Future Development or Transient Trend?
The rise of dual-screen smartphones marks a significant evolution in the realm of mobile technology. These devices present an intriguing proposition by offering two displays within a single handheld unit. The concept taps into the desire for increased functionality, improved multitasking capabilities, and an overall enriched user experience.
The innovative idea behind dual-screen smartphones aims to reimagine how users interact with their devices. It introduces a new dimension to mobile technology by leveraging the potential of multiple screens, which, theoretically, can transform the way we work, consume content, and engage with applications.
The allure of these devices lies in the promise of heightened productivity and efficiency. With two screens at their disposal, users can potentially manage multiple tasks simultaneously. For instance, one screen might serve as a primary display for browsing the web, while the other could handle social media feeds, emails, or act as a supplementary space for note-taking or referencing documents. This potential for multitasking opens doors to seamless workflow management, making these smartphones an appealing choice for professionals seeking enhanced productivity on-the-go.
Moreover, dual-screen smartphones offer an immersive environment for entertainment and gaming. They promise an expansive canvas for indulging in media content, gaming experiences, or creative endeavors, utilizing both screens to deliver a more immersive, cinematic viewing or gaming experience.
However, while the concept of dual-screen smartphones is captivating, its widespread adoption faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the practicality of implementation. Designing devices with dual screens while maintaining portability, durability, and optimal user experience is no simple feat. Achieving a balance between functionality, form factor, and durability remains a significant obstacle for manufacturers.
Additionally, software optimization poses another hurdle. Developing user-friendly interfaces and applications that seamlessly adapt to dual-screen layouts without compromising performance or draining battery life requires careful consideration and development efforts.
The current market showcases diverse approaches to dual-screen smartphones, ranging from devices with foldable screens, detachable modules, or two screens integrated into a single body. While some manufacturers vigorously pursue innovation in this domain, others adopt a more cautious stance, observing consumer reception and market trends before making significant investments.
The future of dual-screen smartphones remains uncertain. Their trajectory hinges on addressing current limitations, refining designs, overcoming technical challenges, enhancing software optimization, and ensuring consumer acceptance. Whether they become a lasting staple in the smartphone industry or remain a passing trend largely depends on technological advancements, consumer preferences, and market dynamics in the years to come.
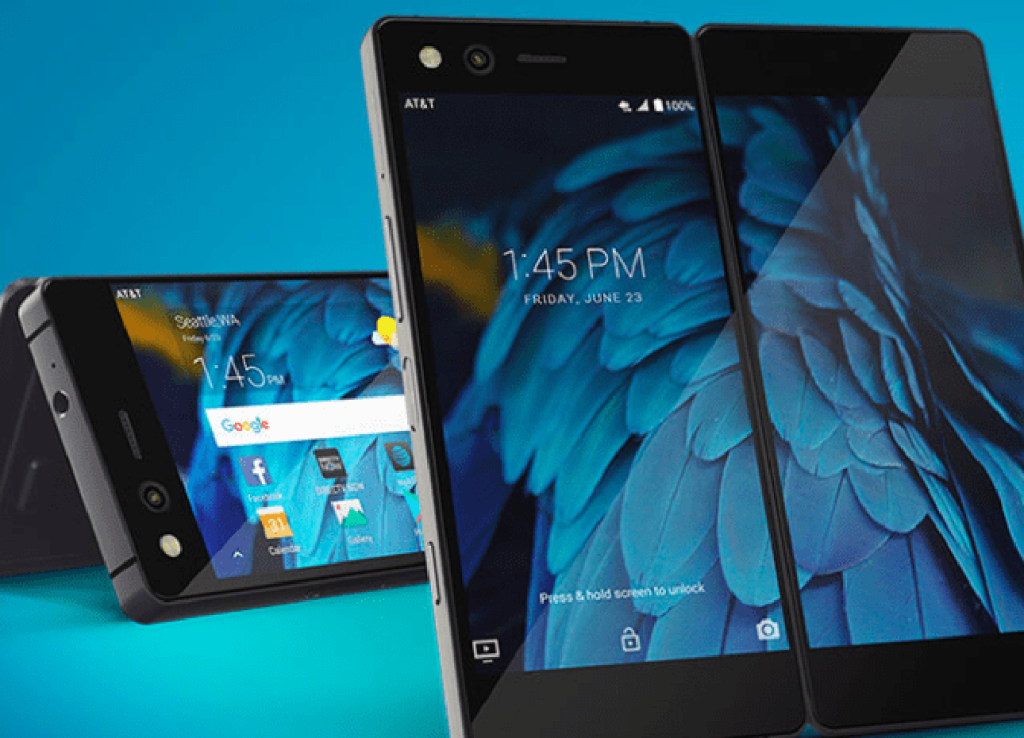

Advantages of Dual-Screen Devices:
Multitasking and Productivity: The primary allure of dual-screen devices lies in their ability to facilitate multitasking. Users can simultaneously run multiple apps or tasks across two displays, streamlining productivity by allowing for efficient multitasking. For instance, professionals can work on documents or emails on one screen while referencing information or browsing the web on the other.
Enhanced User Experience: The additional screen real estate offers a more immersive experience for various activities. Watching videos, browsing content, or playing games benefit from the expanded canvas provided by dual screens. The extended space enables better visibility, improved viewing angles, and enhanced interactivity, enriching the overall user experience.
Versatile Use Cases: The secondary screen serves as a versatile tool, adapting to different use cases. It can function as a dedicated gaming interface, providing additional controls or information while gaming. It can also serve as a quick-access panel for notifications, app shortcuts, or frequently used tools, reducing the need to switch between apps or screens continuously.
Increased Efficiency: Dual-screen devices offer enhanced efficiency, allowing users to organize their workflow more effectively. With the ability to display different apps or content simultaneously, users can streamline tasks, manage workflows, and optimize time spent on various activities.
Innovative Form Factors: These devices often boast innovative designs, including foldable screens, detachable modules, or screens integrated into a single body, showcasing advancements in mobile technology and design aesthetics.
However, despite these advantages, dual-screen devices face notable challenges. They tend to be heavier, bulkier, and more complex in design compared to traditional smartphones. The complexity of implementing dual screens, concerns regarding durability, and the need for seamless software optimization are hurdles that manufacturers must overcome for widespread adoption and market success. Moreover, the added cost of implementing dual screens often results in higher price points, limiting their accessibility to a broader consumer base.
The future of dual-screen devices hinges on overcoming these challenges, refining designs, improving durability, enhancing software optimization, and striking a balance between functionality, portability, and affordability. Their sustained success as a mainstream category in the tech market will heavily rely on addressing these issues and aligning with evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements.
Challenges and Limitations:
Durability and Complexity: Implementing dual screens without compromising durability remains a significant challenge. Foldable or detachable screens are prone to wear and tear, raising concerns about their longevity, especially with continuous folding or unfolding. The complex mechanisms involved in dual-screen designs also raise questions about their robustness over time.
Battery Life: Powering two displays simultaneously poses a challenge to battery life. Maintaining optimal battery performance while driving multiple screens can be demanding, potentially leading to quicker battery drain. Balancing power consumption without sacrificing usability remains a critical aspect for dual-screen devices.
Software Optimization: Ensuring seamless software optimization for dual-screen functionalities and app compatibility is essential. Many applications are yet to fully utilize the potential of dual screens, leading to inconsistent user experiences. Achieving uniformity in app support across dual-screen devices is crucial for providing a cohesive user interface.
Form Factor and Bulkiness: Dual-screen devices, especially those with foldable screens, tend to be bulkier and heavier than traditional smartphones. The challenge lies in striking a balance between offering larger screen real estate and maintaining a manageable form factor that fits comfortably in the user’s hand or pocket.
Higher Cost: The incorporation of dual screens, advanced technology, and innovative designs often results in higher manufacturing costs. As a consequence, dual-screen smartphones typically come with a premium price tag, restricting their accessibility to a broader audience.
Current Market Dynamics:
The tech industry witnesses a blend of cautious optimism and innovative strides concerning dual-screen smartphones. Some manufacturers are committed to refining dual-screen technologies, investing in R&D efforts to improve durability, optimize software experiences, and explore innovative designs.
However, not all manufacturers are rushing to adopt dual-screen designs as a primary focus. Some remain observant of consumer preferences, market trends, and the practicality of dual screens before fully embracing them. This cautious approach allows companies to gauge consumer reception, address existing challenges, and refine their offerings accordingly.
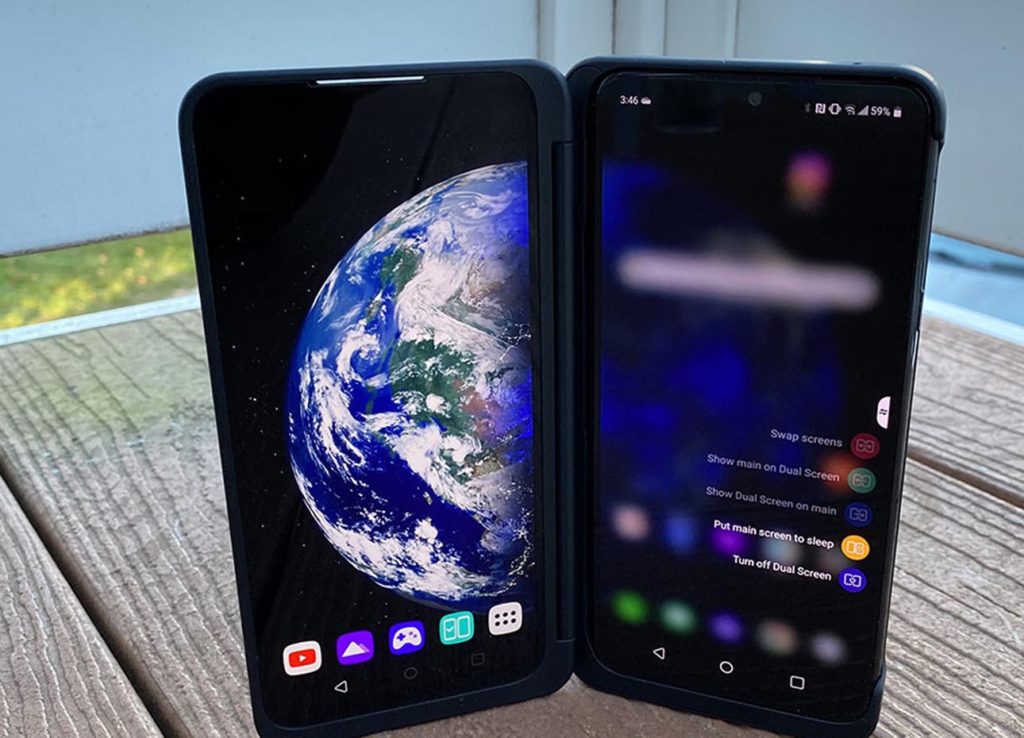

The market’s reception to dual-screen smartphones, therefore, remains a mix of anticipation and careful consideration. The future of these devices hinges on manufacturers overcoming current challenges, refining designs, and addressing consumer concerns while consistently innovating to meet evolving technological demands. Whether dual-screen smartphones will establish themselves as a lasting trend or fade away depends on how effectively these challenges are addressed and how well they resonate with consumers in the long run.
As the tech industry advances, the trajectory of dual-screen smartphones oscillates between innovation and consumer adoption. Undoubtedly, these devices introduce exciting prospects for enhanced productivity, multitasking, and immersive user experiences. However, the journey toward establishing dual screens as a lasting technological norm faces multifaceted challenges that necessitate comprehensive solutions.
The challenges faced by dual-screen smartphones span various crucial aspects. Durability remains a prominent concern, given the intricate mechanisms involved in foldable or detachable screens. Manufacturers must strive to fortify these devices against wear and tear, ensuring that they withstand the test of time while maintaining their functionality.
Battery life presents another hurdle in the path of dual-screen smartphones. Powering two screens simultaneously demands efficient energy management to prevent rapid battery depletion. Achieving an optimal balance between dual-screen functionality and battery endurance remains pivotal in enhancing user experience.
Software optimization constitutes a crucial element for the success of dual-screen devices. Achieving seamless compatibility and utilization of dual screens across diverse applications is essential. The creation of a unified software ecosystem that fully harnesses the potential of dual screens is necessary for delivering a consistent and intuitive user interface.
Furthermore, the form factor and bulkiness of dual-screen smartphones pose challenges. Striking a balance between providing expanded screen real estate and maintaining a convenient and ergonomic design is essential. The devices must offer a comfortable grip while being portable enough for everyday use.
Cost is yet another factor that affects the widespread adoption of dual-screen smartphones. The incorporation of innovative technology inevitably leads to higher production costs, resulting in premium pricing. To broaden consumer accessibility, manufacturers need to explore ways to optimize costs without compromising on quality or essential functionalities.
The current market stance toward dual-screen smartphones reflects a cautious yet optimistic outlook. While certain manufacturers are ardently investing in refining dual-screen technologies, others are taking a more observant stance. This balanced approach allows the industry to assess consumer feedback, address existing challenges, and innovate accordingly.
In essence, the future trajectory of dual-screen smartphones pivots on technological advancements, consumer preferences, and market demands. Overcoming the challenges related to durability, battery efficiency, software optimization, form factor, and cost remains pivotal. Only through concerted efforts, innovative solutions, and consumer-centric designs can dual-screen smartphones solidify their place as a sustainable and enduring innovation in the ever-evolving realm of technology. As these devices continue to evolve and address consumer needs, they have the potential to become a transformative force, shaping the future of mobile technology and user experiences.
